News search
|
Research 11 Apr 2024 CNIC researchers, led by Dr. José Jalife, have made a key discovery about cardiac arrhythmias in Andersen-Tawil syndrome (ATS) |
|
About the CNIC 19 Jan 2024 The ImnovAth project seeks an innovative approach to treat atherosclerosis |
|
Research 21 Dec 2023 Johns Hopkins UniversityBloomberg School of Public HealthBaltimore |
|
About the CNIC 19 Dec 2023 Dr. Carla Rothlin is Dorys McConnell Duberg Professor of Immunobiology and Professor of Pharmacology at the Yale School of Medicine, and co-leader of the Cancer Immunology Programme at Yale Cancer Centre. She studied biochemistry and pharmacology at the University of Buenos Aires, where she also undertook her postgraduate research under the direction of Dr. Ana Belén Elgoyhen, focussing on nicotinic receptors expressed in the inner ear. Later, she completed her doctorate and moved to San Diego to join Dr. Greg Lemke’s laboratory at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies. In 2009, Dr. Rothlin was named Assistant Professor in Immunobiology at Yale Medical School |
|
About the CNIC 17 Nov 2023 This work is of fundamental importance for understanding the immune system and its reactions |
|
About the CNIC 27 Oct 2023 |
|
Research 21 May 2023 The team led by Dr. Pablo García-Pavía, based at the CNIC and Hospital Puerta de Hierro, has published the first study of a drug able to remove amyloid deposits from the heart |
|
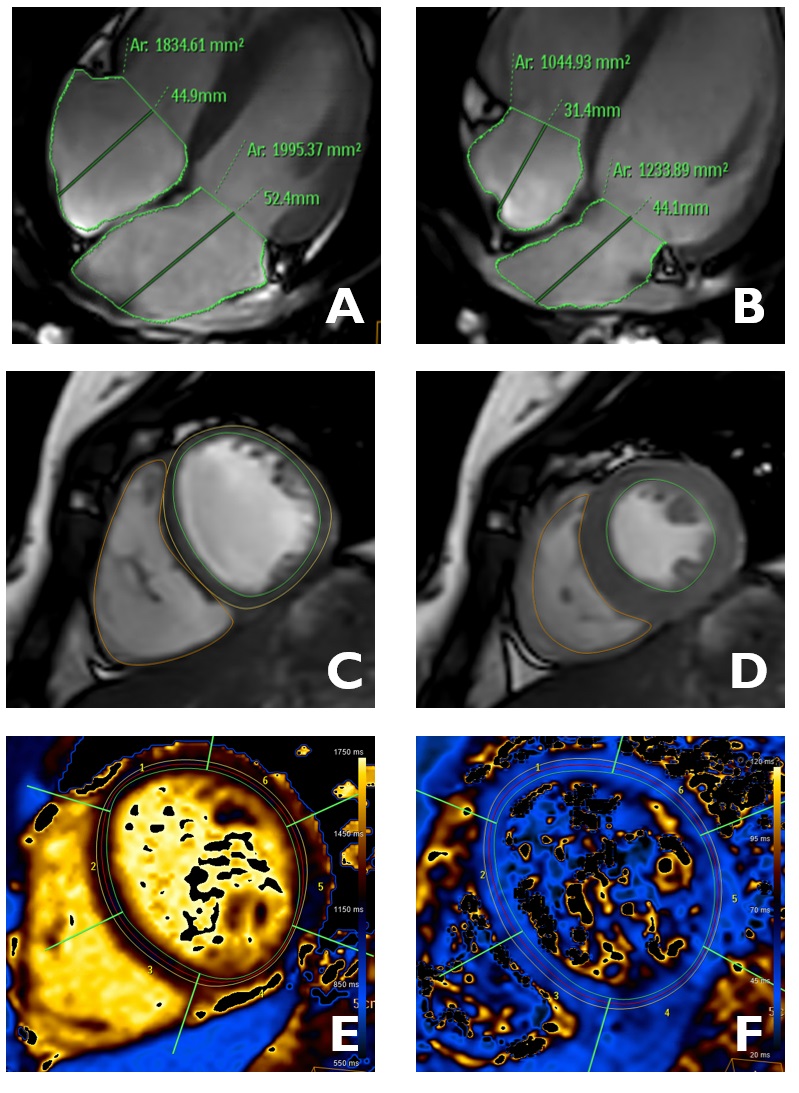
Research 3 Mar 2023 The results, published in eClinicalMedicine, have direct implications for clinical practice by providing a list of reference values for a multitude of cardiac parameters used in daily practice |
|
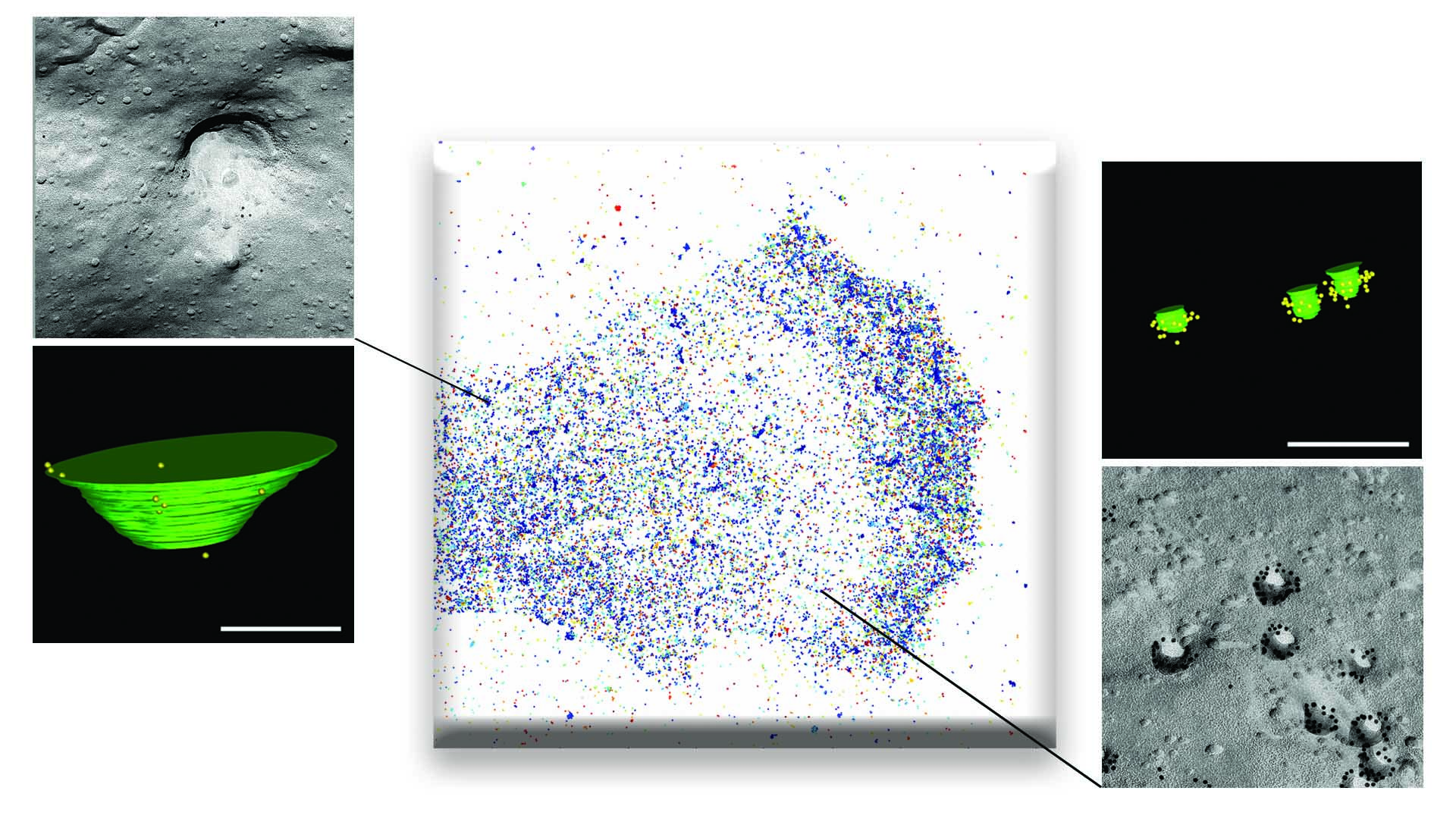
Research 23 Dec 2022 A study published in Nature Cell Biology confirms that caveolae are essential for the mechanical responses of tissues subject to large mechanical forces (such as muscle, heart, blood vessels, and fat), whereas larger membrane depressions (termed 'dolines') are important for the response to weak or medium-strength forces |
|
About the CNIC 23 Nov 2022 |
- 1 of 11
- next ›