Clinical Research
Clinical Research
PESA-Health-CNIC-Santander: Early Detection of Subclinical Atherosclerosis, Disease Progression, and Cardiovascular Health
Principal Investigator: Valentín Fuster
Read more...
The PESA-Health-CNIC-Santander study builds on the foundation laid by its predecessor, the PESA Study, which began in 2010 under the direction of the CNIC in collaboration with Santander Bank. The original study enrolled 4,184 asymptomatic individuals aged 40 to 55 and aimed to detect subclinical atherosclerosis (SA) long before symptoms appear, while also exploring the factors driving its development and progression.
The continuation of the PESA study, PESA-Health, extends this work by tracking the same participants over an additional 10 years. The new study broadens the scope to include new research areas, such as the links between SA and Alzheimer’s disease or cognitive decline, the role of somatic mutations in aging, and how these mutations may influence cardiovascular events and SA progression.
As in the original PESA study, PESA-Health leverages advanced imaging technologies, including 3D vascular ultrasound of the carotid and femoral arteries, coronary computed tomography, cardiac magnetic resonance, and whole-body positron emission tomography. In addition, biosampling is used for for extensive omics analysis. Polysomnographic studies and accelerometers are used to study sleeping patterns and physical activity.
As the CNIC’s flagship study, PESA-Health involves many of the center’s clinical and basic research groups. Findings from the PESA study have already made significant contributions to understanding the origins and progression of atherosclerosis.
Early in 2025, the fifth visit of the study was started.

RESILIENCE: REmote iSchemic condItioning in Lymphoma PatIents REceiving ANthraCyclinEs
Principal Investigator: Borja Ibáñez
H2020 Grant# 945118
Read more...
Anthracyclines are a widely used class of anticancer drugs, administered to over 3 million of the 4 million new cancer patients diagnosed annually in Europe. While effective, these drugs carry a significant risk: recent data show that >35% of patients treated with anthracyclines develop some form of cardiomyopathy. This trade-off between cancer treatment and chronic heart failure (HF) not only places a heavy psychological burden on cancer survivors but also poses a growing challenge for healthcare systems.
Remote ischemic conditioning (RIC) offers a potential solution. RIPC is a noninvasive, safe, and cost-effective technique that involves brief, reversible episodes of ischemia (e.g., in an arm) followed by reperfusion. This process can protect remote tissues and organs against injury in future ischemic events. Experimental studies in large animals have shown that 3 to 5 cycles of 5-minute limb ischemia followed by 5-minute reperfusion reduce the size of induced myocardial infarctions. Recent evidence suggests that, to be effective, RIC must be initiated before the damaging event. Since chemotherapy is a planned procedure, anthracycline-induced cardiomyopathy provides an ideal setting to test this approach.
RESILIENCE is a multinational, phase II, double-blind, sham-controlled, randomized controlled trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of RIPC in patients with lymphoma or breast cancer and who are receiving anthracyclines. Eligible patients scheduled to receive ≥240 mg/m² of anthracyclines undergo baseline cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging and blood tests for high-sensitivity troponin (hsTn) and NT-proBNP. Patients with a left ventricular ejection fraction >40% confirmed by CMR are randomized 1:1 to receive either RIPC or a sham procedure.
Nine weeks after completing chemotherapy, patients undergo a final CMR and hsTn/NT-proBNP test. Clinical follow-ups are scheduled for 12, 18, 30, and 42 months until the last patient completes the final CMR.
The RESILIENCE Trial aims to enroll 608 patients across 22 sites in six European countries (Spain, Portugal, France, Germany, the Netherlands, and Denmark). Funded by the European Commission (Grant Agreement-945118-RESILIENCE), the trial began its grant period in June 2021, with patient recruitment starting in 2022. By the end of 2024, three additional hospitals were added, all 22 sites were operational, and 284 participants had been enrolled.

REBOOT: TREatment with Beta-blockers after myOcardial infarction withOut reduced ejection fracTion
Principal Investigator: Borja Ibáñez
H2020 Grant#945118
Read more...
The use of beta-blockers for patients after a myocardial infarction (MI) is largely based on evidence from trials conducted before the reperfusion era. While these drugs have proven benefits for post-MI patients with reduced ejection fraction, their effectiveness for patients with preserved ejection fraction remains unclear. Despite this lack of evidence, over 80% of post-MI patients in this category are prescribed beta-blockers for life.
The REBOOT trial addresses this gap by evaluating the need for beta-blocker therapy in post-MI patients with a left ventricular ejection fraction greater than 40%. This multinational study has enrolled 8,505 patients since 2018 to 2024, who have been randomized to either receive beta-blockers (with the type and dose determined by their physician) or no beta-blocker treatment. The primary endpoint is a composite of all-cause death, reinfarction, or heart failure admission over a median follow-up almost 4 years.
Coordinated by the CNIC Clinical Trials Coordination Unit and conducted in collaboration with the Mario Negri Institute of Pharmacological Research in Milan, the trial involves 77 hospitals in Spain and 32 in Italy. This large-scale project has the potential to significantly influence clinical practice.
Results will be made public during the ESC congress 2025 in Madrid.

MRVALVE: Multimodality Myocardial Tissue Characterization in Patients with Significant Valvular Disease
Principal Investigator: Borja Ibáñez
Read more...
The MRVALVE study uses a multimodality imaging approach (cardiac magnetic resonance [CMR] and strain echocardiography) to better characterize left ventricular (LV) status in patients with significant valvular heart disease (VHD), focusing on aortic valve stenosis (AS) as a model of LV pressure overload and mitral regurgitation (MR) as a model of LV volume overload.
VHD significantly impacts LV dimensions, function, and tissue composition, all of which play a critical role in clinical decision-making. Current guidelines recommend surgical treatment for patients with significant VHD when symptoms develop or when there is evidence of LV remodeling or dysfunction. The most common forms of VHD are AS and MR. The progression from asymptomatic to symptomatic disease, or from normal LV function to LV dilatation, hypertrophy, and dysfunction, is driven by changes in tissue composition—primarily cardiomyocyte death, extracellular volume expansion, and fibrosis.
While surgery or percutaneous valve repair or replacement are effective treatments for severe VHD, interventions are typically based on the presence of symptoms or significant LV dysfunction. By the time these features appear, it is often too late to fully restore heart function. This highlights the need for tools for the early detection of myocardial involvement in asymptomatic VHD patients, allowing timely intervention before irreversible damage occurs.
CMR is the gold standard for anatomical and functional cardiac assessment. This methodology can detect focal fibrosis through late gadolinium enhancement and offers advanced tissue characterization using techniques like parametric T1/T2 mapping, absolute myocardial perfusion quantification, and extracellular volume calculation (a marker of diffuse fibrosis). These assessments require the use gadolinium-based contrast agents, which have a strong safety profile and are widely used in clinical practice. A blood sample is also needed to determine hematocrit for assessing diffuse fibrosis.
Strain echocardiography, the best imaging modality for evaluating active LV myocardial deformation, can detect impaired multidirectional strain even when overall LV function appears normal. In the MRVALVE study, we correlate imaging data with functional assessments from the 6-minute walking test, which provides an objective measure of exercise capacity. Additionally, cardiac computed tomography is used to assess calcium deposition in the coronary arteries and heart valves, providing a calcium score that serves as both a diagnostic and prognostic tool in AS patients.
To date, 71 patients have been recruited, and all have completed their 1-year follow-up visit.
MATRIX: Novel Mitochondria-targeted Therapies for Cancer Treatment–induced Cardiotoxicity
Principal Investigator: Borja Ibáñez
ERC Consolidator Grant#819775
Read more...
The MATRIX Project aims to develop innovative treatments for cardiotoxicity caused by certain cancer therapies. This initiative is a joint effort between the CNIC and Fundación Jiménez Díaz University Hospital, building on a collaborative framework established in 2015 to study myocardial diseases.
While significant advances in cancer treatment have improved outcomes for the 4 million new cancer patients diagnosed annually in Europe, these therapies often come with serious side effects. One of the most common is cancer treatment–induced cardiotoxicity (CTiCT), which affects up to 25% of patients treated with anthracyclines or trastuzumab. CTiCT can lead to severe complications, including chronic heart failure or even death, creating a devastating trade-off for cancer survivors.
CTiCT poses a significant challenge, as current therapies are suboptimal. Early detection methods are inadequate, and heart failure treatments are nonspecific. Recent findings from our group suggest that CTiCT is linked to altered mitochondrial dynamics, which triggers metabolic reprogramming in cardiomyocytes.
The MATRIX Project takes a holistic approach to addressing mitochondrial dysfunction in CTiCT. We propose that early-stage CTiCT could be reversed by metabolic reprogramming to alter mitochondrial substrate utilization. Using a novel imaging-based algorithm developed by our team, we aim to detect myocardial damage in patients receiving common anticancer drugs long before traditional clinical parameters show abnormalities. This early detection, currently unavailable, is critical for timely intervention.
For end-stage CTiCT, where mitochondrial dysfunction may be irreversible, we propose that replenishing the myocardium with healthy mitochondria through in-vivo mitochondrial transplantation could offer a radical new therapeutic option.
The MATRIX Project has broad translational potential, including the development of new therapeutic approaches, early diagnostic technologies, and insights into the basic mechanisms of CTiCT.
Patient recruitment began in 2020, and as of February 2025, 56 participants have been enrolled.

MYOCARDITIS-CNIC: Prospective Registry to Validate a New Diagnostic Marker in Patients with Clinical Suspect of Myocarditis
Principal Investigator: Pilar Martín Fernández
Co-Principal Investigator: Domingo Pascual Figar
Read more...
Acute myocarditis is challenging to diagnose due to its varied clinical presentation and the lack of rapid, accessible, and accurate diagnostic tools. Symptoms can range from atypical chest pain (resembling pericarditis or angina) to dyspnea, fatigue, palpitations, syncope, and, in severe cases, sudden death or shock. Early diagnosis is further complicated by the nonspecific results obtained with standard tests, such as ECG, echocardiography, and laboratory tests.
Currently, diagnosing acute myocarditis typically requires invasive procedures like endomyocardial biopsy or advanced imaging techniques like cardiovascular magnetic resonance, which are not universally available. This highlights the urgent need for new, noninvasive diagnostic approaches.
Dr. Martín Fernández’s research group has made significant progress in this area by identifying a novel microRNA in mice and humans with myocarditis. Their work, published in the New England Journal of Medicine (2021: 27;384(21):2014-2027), demonstrates that the human homolog (hsa-miR-Chr8:96) can effectively distinguish myocarditis patients from those with myocardial infarction.
The MYOCARDITIS-CNIC Registry, a collaborative initiative between the CNIC and Hospital Virgen de la Arrixaca, aims to build on these findings. Several Spanish hospitals, including Hospital de la Princesa and Clínica Universitaria de Navarra, are participating in the registry by collecting clinical data and biological samples from patients presenting to emergency departments with signs of myocarditis. This registry will provide critical insights into the early stages of myocarditis and help validate potential clinical biomarkers for early diagnosis.
To date, 75 participants have been enrolled in the registry.
PRECOGNITIVE: Effect of Remote Ischemic Preconditioning on Cognitive Function and Cerebral Vasculature
Principal Investigator: Gonzalo Pizarro Sánchez
Read more...
Arterial hypertension can cause damage to the cerebral vascular system, even when blood pressure effectively controlled. Current treatments for hypertension focus on managing blood pressure and preventing damage to target organs, such as the brain. Remote ischemic preconditioning (RIPC), a technique first shown to protect organs like the heart and brain in animal models 30 years ago, has since been adapted for use in human patients. RIPC involves inflating and deflating a blood pressure cuff on the arm through four cycles of 5 minutes each. The brief ischemia induced in the arm can protect distant organs, including the brain, from future ischemic damage.
Our research group has contributed significantly to this field, with recent studies demonstrating that RIPC can improve cognitive performance and cerebral vascular function in patients with vascular dementia.
The PRECOGNITIVE study is a proof-of-concept randomized trial involving 45 women with hypertension and evidence of target organ damage, such as left ventricular hypertrophy. Participants are divided into 3 groups:
- The RIPC group undergo the RIPC procedure, with the cuff inflated to 20 mmHg above their systolic blood pressure.
- The RIPC-Sham group follow the same procedure, but the cuff will only be inflated to 50 mmHg, insufficient to induce ischemia.
- The control group do not receive any cuff therapy.
The study aims to determine whether RIPC has a significant protective effect on the cerebral vasculature in hypertensive patients without significant cognitive impairment. Outcomes will be assessed using comprehensive neurocognitive tests and noninvasive imaging techniques, including echocardiography, noncontrast brain magnetic resonance imaging, and transcranial Doppler ultrasound.
As of the end of 2024 15 patients have been recruited.
MACADAMIA: Characterization of Cardiac Metabolism Using Multimodal Imaging in Idiopathic Cardiomyopathy
Principal Investigator: Borja Ibáñez
Read more...
Heart failure (HF) is one of the most significant health challenges in modern societies, placing a heavy burden on healthcare systems. To develop new therapies, it is essential to understand the mechanisms underlying the development and progression of HF.
The heart is the body’s most energy-demanding organ relative to its size. Under normal conditions, it primarily relies on fatty acid beta-oxidation, which generates about 60% of the ATP needed for cardiac function. Carbohydrate metabolism via the Krebs cycle provides the second-largest energy source, while other nutrients, such as amino acids, contribute less than 1%.
In HF, however, the heart undergoes a metabolic shift, switching from fatty acids to glucose as its main energy source. This phenomenon, known as the metabolic switch, was initially thought to be a protective adaptation. However, recent evidence from animal and human studies shows that glucose metabolism produces 4-5 times less ATP than fatty acid metabolism, suggesting that this switch is harmful and contributes to the decline in cardiac contractile function.
Our group has demonstrated that the metabolic switch plays a key role in the progression of HF secondary to idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy (IDCM). In mouse models, a diet rich in fatty acids reversed the metabolic switch and improved the IDCM phenotype. Similar results were observed in pigs, which have a metabolism comparable to humans.
Before conducting a clinical trial in patients with IDCM, it is critical to determine the prevalence of the metabolic switch in this population. This is the primary goal of the MACADAMIA study, an observational project involving a small cohort of IDCM patients. Using advanced imaging techniques—including transthoracic echocardiography with myocardial strain analysis, cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR), and positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) with the radiotracer 18FDG—the study aims to characterize the metabolic profile of these patients without any intervention.
As of February 2025, 28 patients have been recruited. In the medium to long term, we plan to conduct a clinical trial in IDCM patients who exhibit the metabolic switch. Patients will be randomized to receive either a diet rich in fatty acids or a normal diet, and will be assessed for changes in cardiac function (by CMR) and metabolism (by PET/CT).
ATTRACKING CNIC: The ATTRACKING Registry
Principal Investigator: Pablo García Pavía
Read more...
Tafamidis is a medication used to treat transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis (ATTR-CM), a rare and life-threatening disease caused by the buildup of of transthyretin amyloid fibrils in the heart. Clinical trials have demonstrated that Tafamidis reduces mortality and cardiovascular hospitalizations in patients with ATTR-CM, prompting its recent approval for use in Spain. However, clinical trials can have limitations, and their results may not always reflect real-world clinical outcomes.
Advances in diagnostic techniques have enabled earlier detection of ATTR-CM, resulting in a shift in patient profiles and improved prognoses compared with the population studied in the original clinical trial. This raises questions about the effectiveness and safety of Tafamidis in contemporary patients. The ATTRACKING CNIC study aims to address this uncertainty by evaluating Tafamidis in a real-world, unselected cohort of ATTR-CM patients.
Objectives
- To characterize the real-world population of ATTR-CM patients in Spain prescribed 61mg Tafamidis.
- To assess the safety of Tafamidis in a diverse, real-world Spanish cohort with ATTR-CM.
- To compare the real-world clinical impact of Tafamidis therapy with the results of the ATTR-ACT clinical trial.
Study Design
ATTRACKING CNIC is a prospective, multicenter, non-randomized observational trial involving patients diagnosed with ATTR-CM who are starting daily treatment with 61 mg Tafamidis.
As of February 2025, contracts have been signed with 22 hospitals, and 195 participants have been recruited.

TAILOR-AF: Patient-specific Ablation of Persistent Atrial Fibrillation Drivers Guided by Frequency and Amplitude Modulation Criteria
Principal Investigator: David Filgueiras
Co-Promoters: Hospital Universitario Clínico San Carlos / Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares Carlos III (F.S.P.)
Read more...
Pulmonary vein isolation (PVI) is the cornerstone of catheter-based ablation for patients with persistent atrial fibrillation (AF). However, over the past 20 years, the success rate of PVI in achieving long-term rhythm control for persistent AF has been suboptimal. Even with treatment, only about 40% of patients remain free of AF (without antiarrhythmic drugs) at 12 months post-ablation, highlighting the challenges of managing this condition.
To address this issue, our group has developed a computational tool that helps interventional electrophysiologists identify specific atrial regions, called driver regions, which are associated with the long-term persistence of AF. Using a conventional electroanatomic mapping system and multielectrode catheters, these regions can be pinpointed with novel signal processing algorithms. These algorithms, which are openly available to the scientific community (Quintanilla JG et al. Circ Res. 2019;125:609-27), analyze individual atrial signals to detect frequency and amplitude modulations (iFM and iAM) during fibrillatory activity. This allows for the precise localization of rotational activity and the identification of the leading drivers of persistent AF.
The primary goal of the TAILOR-AF study is to use iAM/iFM mapping to identify and ablate the leading drivers of AF in patients who continue to experience symptomatic recurrences of persistent AF despite undergoing 2 or more PVI procedures. Secondary objectives include analyzing blood biomarkers, atrial imaging parameters, and phenotypic features in the surface electrocardiograms associated with advanced atrial remodeling. In patients undergoing minimally invasive thoracoscopy-guided ablation of leading drivers, tissue samples from the left atrial appendage will also be collected to study the molecular mechanisms underlying AF maintenance.
As of the end of 2024, 22 patients had been enrolled in the study.
SIR-CVT: Spanish Immunotherapy Registry – Cardiovascular Toxicity
Co-Promoters: Sociedad Española de Cardiología / Sociedad Española de Oncología Médica / Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares Carlos III (F.S.P.)
Read more...
SIR-CVT is a non-interventional project with two primary objectives:
- To evaluate risk factors and current practice management practices for cardiovascular (CV) toxicity in patients with solid organ cancer receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) for approved indications.
- To validate the human homolog of miR-721 as a biomarker for the early diagnosis of immunotherapy-induced myocarditis in these patients.
The study also addresses several secondary objectives:
- Identifying clinical, electrocardiographic, imaging, laboratory, and genetic markers for the early diagnosis of ICI-related myocarditis.
- Identifying markers for the early detection of other ICI-related adverse CV effects unrelated to myocarditis.
- Evaluating the relationship between previous chemotherapy regimens and ICI-related CV risk.
- Investigating the pathogenic mechanisms underlying myocarditis induced by immune checkpoint blockade (antiPD-L1/PD1 and anti-CTLA4).
- Assessing the impact of CV monitoring on patient quality of life and perceived quality of care.
The study involves of a baseline visit, after which patients are managed according to standard clinical protocols, including the frequency of follow-up visits. Participants will be followed until death, loss to follow-up, or the final visit 12 months after enrollment. All data collected will be used exclusively for research purposes.
As of February 2025, two patients have been enrolled and have undergone cardiac magnetic resonance and ultrasound imaging studies at the CNIC.

REACT: Reversal of Early Atherosclerosis through Personalized Curative Treatment
Principal Investigator: Borja Ibáñez
Funded by Novo Nordisk Foundation
Read more...
Atherosclerosis, the buildup of plaque in arteries, is the leading cause of cardiovascular diseases. This condition develops gradually as cholesterol, fat, blood cells, and other substances accumulate in the arterial walls, causing them to narrow and reducing blood flow to vital organs. Atherosclerosis contributes significantly to global morbidity and mortality, often beginning early in life and affecting multiple vascular systems.
To address this major health challenge, the CNIC and the Rigshospitalet in Copenhagen have launched Phase 1 of the REACT project (Reversal of Early Atherosclerosis through Personalized Curative Treatment), funded by the Novo Nordisk Foundation. The primary goal of this phase is to determine the prevalence of asymptomatic (silent) atherosclerosis in a diverse, European-ancestry population across a wide age range (18–69 years). This will be achieved using advanced biomedical imaging techniques and circulating biomarkers, alongside traditional risk factors.
The REACT project focuses on early detection of atherosclerosis through a combination of imaging techniques, including vascular ultrasound (3DVUS), calcium scoring, and angiography, as well as biomarker analysis. The first phase is a prevalence study involving 16,000 participants (8,000 in Spain and 8,000 in Denmark). This study will provide a detailed understanding of how common asymptomatic atherosclerosis is at different ages and help develop a more precise risk evaluation algorithm than those currently in use.
The findings from Phase 1 will inform the design of Phase 2, a randomized clinical trial that will assess whether early intervention—guided by imaging and including lifestyle changes, non-pharmacological approaches, and lipid-lowering treatments—can reduce atherosclerotic plaque burden or even lead to regression or cure.
Enrollment started in January 2025. As in June 2025, 2,500 subjects have been enrolled in Spain (5,000 overall). This initiative will create a unique resource for future basic and clinical research.

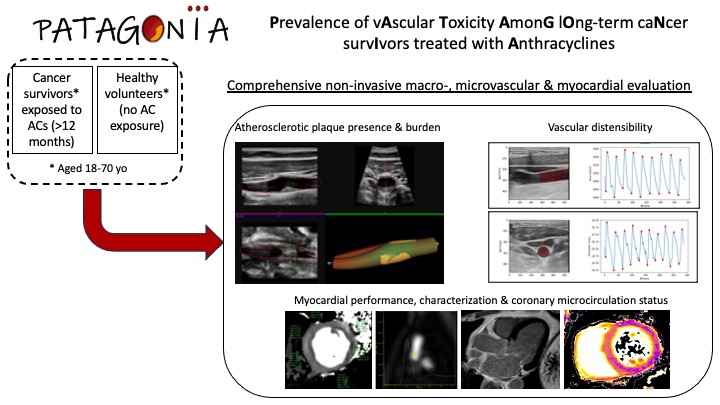
PATAGONIA: Prevalence of vAscular Toxicity AmonG lOng-term caNcer survIvors treated with Anthracyclines
Project "PI24/00260", funded by Instituto de Salud Carlos III (ISCIII) and co-funded by the European Union.
Principal Investigator: Inés García Lunar
Read more...
Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) and cancer are the two main causes of mortality and are frequently associated. Anthracyclines (ACs), a family of chemotherapy drugs that are used to treat a wide number of tumors, are the primary agents responsible for chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity. The mechanisms that lead to cardiac toxicity due to ACs are not yet fully understood, nor are there any specific interventions with proven efficacy to prevent cardiac damage. The effect of ACs on the myocardium has been subject of extensive research over the past years. Nevertheless, one of the most intriguing aspects of AC-induced cardiotoxicity is that ventricular function is sometimes preserved during and immediately after chemotherapy, but the myocardium may become vulnerable to subsequent stressors, causing problems later in life. Strong evidence from both experimental studies and early clinical observations suggests that ACs may cause damage to the vasculature before the onset of cardiac dysfunction. Our hypothesis is that this mechanism (vascular involvement) could remain latent for a prolonged period of time and contribute to the development of AC-induced cardiomyopathy and, ultimately, heart failure years later.
PATAGONIA aims to study in long-term cancer survivors the vascular consequences of prior treatment with ACs and the risk factors associated with the onset of late vascular and myocardial toxicity using non-invasive imaging technology.
This is a multicenter, retrospective cohort study including 2 groups: subjects previously exposed and not exposed to ACs. Inclusion criteria for the exposed cohort will be patients aged 18 to 70 years with a past medical history of cancer (hematological or solid) and prior AC treatment. Subjects with history of clinical CVD or left ventricular systolic dysfunction will be excluded. Non-exposed subjects will be asymptomatic individuals without history of cancer or CVD. A comprehensive non-invasive imaging study using state-of-the-art technology will be undertaken, including a stress cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) to calculate the coronary flow reserve as a surrogate of the coronary microcirculation status (primary outcome measure) as well as vascular ultrasound of peripheral arteries (carotids and femorals) to measure atherosclerotic plaque burden and vascular distensibility. Statistical analyses will include adjustment for other potentially confounding variables such as age, sex, concomitant thoracic radiotherapy, time since the end of treatment, total AC dose and presence of cardiovascular risk factors or other potentially cardiotoxic treatments.
This project may result in new tools for early detection of cardiac damage secondary to AC treatment, thus being able to improve prevention of CVD in patients with a history of cancer.

Cardiac metabolic reprogramming by a nutritional intervention: the High Fat Diet for Heart Failure (HF4HF) study, a proof-of-concept randomized controlled trial
Horizon Europe, ERA4Health. Grant#101095426
Read more...
The "High Fat Diet for Heart Failure" (HF4HF) study is a proof-of-concept randomized controlled trial designed to investigate the efficacy of a high-fat diet (HFD) as a therapeutic intervention in patients with non-ischemic dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) and reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF). The study hypothesizes that cardiac metabolic reprogramming, achieved through a controlled nutritional intervention involving an HFD, can enhance systolic function, myocardial energetics, and overall heart function in heart failure (HF) patients. Co-funded by the European Commission and national entities, the trial is spearheaded by a consortium of cardiovascular research centers across four countries: Spain, Italy, France, and Romania.
We hypothesize that high-fat diet (HFD) over a two-month period will lead to a significant improvement in LVEF compared to a standard diet.
A HFD will improve myocardial energetics, diastolic function, and left ventricular strain parameters without causing adverse effects on lipid profile or liver function.
The HF4HF trial is a multicenter, multinational, two-arm, parallel, randomized controlled trial. A total of 80 patients diagnosed with non-ischemic DCM and reduced LVEF will be recruited from four European centers. These patients will be randomized into two groups: one receiving a HFD and the other a control diet with standard macronutrient breakdown.
The trial is classified as a prospective, randomized, open, blinded-endpoint (PROBE) trial, meaning that while participants and healthcare providers will not be blinded to treatment allocation, outcome assessors will remain blinded.
The study will include men and women over the age of 18 with a confirmed diagnosis of non-ischemic DCM and LVEF ≤40%. Patients with established atherosclerosis, uncontrolled dyslipidemia, or contraindications for CMR will be excluded. After the initial screening, eligible participants will be randomized in a 1:1 ratio to either the HFD group or the control group.
The HFD group will receive a diet composed of 70% of their daily caloric intake from fats, primarily sourced from nuts, olive oil, avocados, fish, and cheese. Protein will account for 10-20% of the diet, with the remainder from carbohydrates. In contrast, the control group will follow a diet with 30% of caloric intake from fats, 10-20% from protein, and 50-60% from carbohydrates.
The dietary intervention will last two months, during which patients will be closely monitored for adherence and side effects. After the intervention, patients will be followed for another two months to assess the sustainability of the effects post-intervention.
Dapagliflozin after Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation
Principal Investigator: Sergio Raposeiras-Roubin (Hospital Álvaro Cunqueiro Vigo)
Principal Investigator CNIC: Borja Ibáñez
Read more...
Aortic valve stenosis (AS) is a progressive disease in which the final stage is characterized by obstruction of the left ventricular outflow tract, resulting in insufficient cardiac output, reduced exercise capacity, heart failure (HF), and death from cardiovascular causes. The prevalence of AS is only about 0.2% among adults aged 50 to 59 years but increases to 9.8% in octogenarians, with an overall prevalence of 2.8% in adults over 75 years old. While mortality does not increase when AS is asymptomatic, the mortality rate exceeds 50% at 2 years for patients with symptomatic disease unless aortic valve replacement (AVR) is performed promptly. AS is a slowly progressive disease but is associated with a poor prognosis a few years after the onset of symptoms if not treated with aortic valve replacement (AVR). Surgical aortic valve replacement had been the only effective treatment for severe AS for many years. However, transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) has emerged as an effective alternative to surgical replacement, showing short- and mid-term outcomes comparable to, or even better than, surgical techniques regardless of patients' surgical risk. Moreover, the pathophysiology of HF suggests that dapagliflozin, a sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT-2) inhibitor, may be valuable in the treatment of HF regardless of the presence or absence of diabetes mellitus (DM).
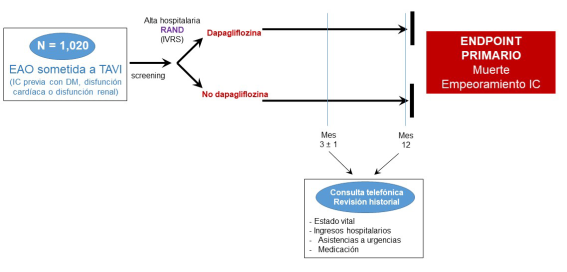
The primary objective of the DapaTAVI trial was to investigate the effects of dapagliflozin treatment on mortality and the risk of HF readmission in patients with severe AS and a previous HF hospitalization who undergo TAVI and have one of the following three conditions: DM, left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) ≤ 40%, or renal dysfunction (eGFR 25–75 ml/min/1.73 m²).
DapaTAVI is a pragmatic, prospective, randomized, open-label, controlled clinical trial with blinded endpoint evaluation (PROBE design). Patients who are discharged after undergoing TAVI and meet all inclusion criteria and none of the exclusion criteria were eligible to participate in the study. Patients have been randomized 1:1 into one of the following two arms:
- Intervention group: Treatment with a daily oral dose of dapagliflozin 10 mg.
- Control group: No treatment with dapagliflozin.
Apart from dapagliflozin therapy (or control), patients have been treated according to current guidelines and based on the clinical judgment of their attending physician.
Results: A total of 620 patients were randomly assigned to receive dapagliflozin and 637 to receive standard care alone after TAVI; after exclusions, a total of 1222 patients were included in the primary analysis. A primary-outcome event occurred in 91 patients (15.0%) in the dapagliflozin group and in 124 patients (20.1%) in the standard-care group (hazard ratio, 0.72; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.55 to 0.95; P = 0.02). Death from any cause occurred in 47 patients (7.8%) in the dapagliflozin group and in 55 (8.9%) in the standard-care group (hazard ratio, 0.87; 95% CI, 0.59 to 1.28). Worsening of heart failure occurred in 9.4% and 14.4% of the patients, respectively (subhazard ratio, 0.63; 95% CI, 0.45 to 0.88). Genital infection and hypotension were significantly more common in the dapagliflozin group.
Conclusions: Among older adults with aortic stenosis undergoing TAVI who were at high risk for heart-failure events, dapagliflozin resulted in a significantly lower incidence of death from any cause or worsening of heart failure than standard care alone. (Funded by Instituto de Salud Carlos III and others; ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT04696185.).
N Engl J Med. 2025 Apr 10;392(14):1396-1405. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa25003663333.







