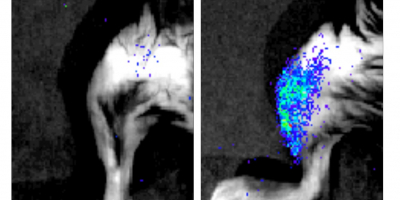
A study published in Nature Cardiovascular Research reveals smooth muscle-derived cells as a new target for reducing the size of atherosclerotic plaque. The results open up new avenues for the design of treatments to enhance the beneficial effect of cholesterol-lowering drugs
The most potent genetic risk factor for Alzheimer disease, APOE4, is associated with an elevated risk of developing subclinical atherosclerosis in middle age, whereas the Alzheimer-protective variant of the same gene, APOE2, protects against subclinical atherosclerosis
A new CNIC study shows that low-grade systemic inflammation triggered by subcinical atherosclerosis accelerates epigenetic aging in otherwise healthy young individuals
The finding provides a basis for mitigating the loss of muscle regenerative capacity in elderly people and for improving muscle repair in young healthy people