News search
|
Research 15 Dec 2022 A CNIC team has shown that the retinoid and unsaturated fatty acid sensor RXR is a key protein in the maintenance of a balanced production of the different types of blood cells |
|
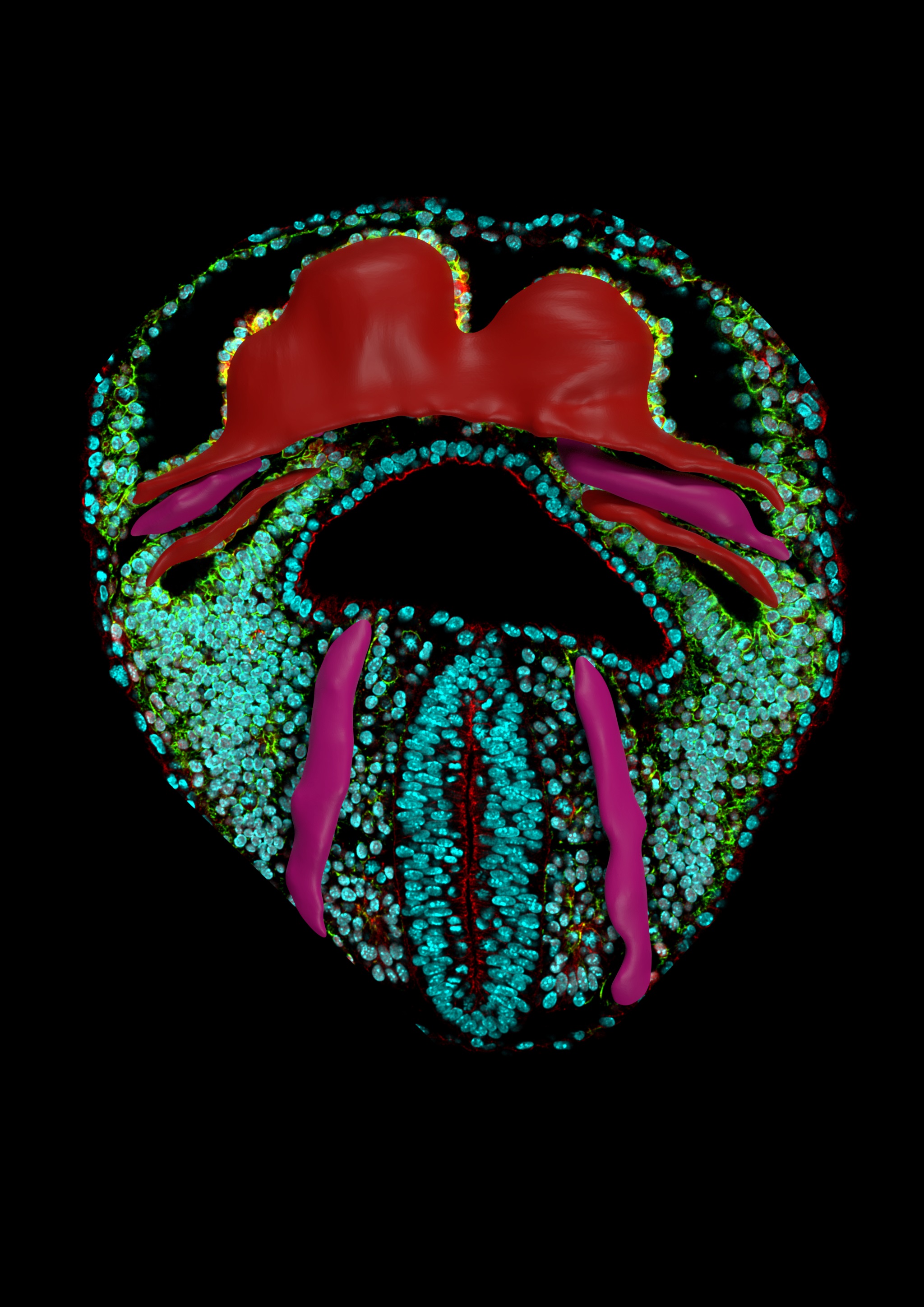
Research 17 May 2022 The 3D atlas has allowed the scientists to identify the beginning of left–right asymmetry in the heart |
|
Research 18 Apr 2022 The research will provide insights into the development of potential treatments for neurological diseases and obesity, among other human conditions |
|
Research 9 Dec 2020 Científicos del CNIC han descubierto un mecanismo celular y molecular que puede ayudar a promover la arterialización y perfusión en los tejidos que han sufrido una reducción del riego sanguíneo. |
|
Research 1 Feb 2018 The researchers have identified a collection of almost 300 genes mutated by AID, with some of the mutations found recurrently in human tumors and lymphomas |
|
Research 25 Nov 2016 The study describes a cell signal that controls intercellular communication and could play a central role in biomedical strategies such as gene therapy, vaccine design, and immunotherapy |
|
About the CNIC 9 Jan 2013 En un trabajo previo, parte de los investigadores mostraron que ratones deficientes en el gen Polµ presentaban una capacidad reducida de reparación del daño celular y eran radiosensibles |
|
Publications 10 Sep 2012 |