Computational Systems Biomedicine
Overview
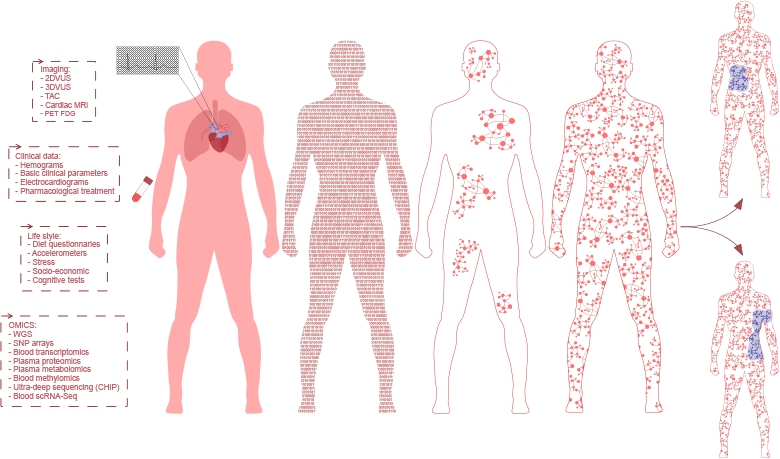
The Computational Systems Biomedicine Lab develops multimodal artificial intelligence approaches to advance biomedical research, with a particular focus on cardiovascular disease. Our work integrates molecular omics, clinical records, and imaging data from large cohorts of healthy individuals to create computational digital twins—virtual replicas that model the progression of health and disease at the individual and population levels.
Our research builds on three foundational pillars—Big Biomedical Data, Advanced Algorithmics and AI, and High-Performance Computing—which together enable scalable, reproducible, and clinically meaningful computational models for precision cardiovascular medicine.
Vision
Our vision is to transform cardiovascular medicine through the creation of intelligent, data-driven digital twins that capture the complexity of human biology across molecular, clinical, and imaging domains. By uniting large-scale biomedical data with advanced computational modelling, we aim to enable earlier detection of disease, personalized prevention strategies, and more effective therapeutic decision-making. We aspire to help build a future in which precision cardiovascular health is accessible, proactive, and equitable for all.
Mission
Our mission is to advance the scientific and technological foundations of multimodal AI for biomedicine. We develop scalable algorithms, rigorous data infrastructures, and interpretable models that generate actionable insights into cardiovascular health and disease. Through interdisciplinary collaboration, adherence to FAIR and ethical data principles, and a commitment to open scientific innovation, our lab seeks to empower clinicians, policymakers, and researchers with tools that improve population health and individual care.
Research Axes
1. Big Biomedical Data
We develop the infrastructure, standards, and platforms needed to support next-generation cardiovascular digital twins.
Key Projects
- Standardization and Harmonization Guidelines for CVD and Diabetes
Creation of unified protocols for data collection, integration, and sharing across molecular, clinical, and imaging modalities. - EUROCARDIAB: A Federated Pan-European Platform
A secure, federated environment integrating cardiovascular health indicators across Europe.
Central features include:- CVD Impact Simulator: Models how modifying risk factors influences disease prevalence and outcomes.
- Intelligent Policy Agent (IPA): An AI system capable of autonomously analyzing epidemiological trends, simulating intervention impact, and generating synthesized policy briefings for healthcare decision-makers.
- CNIC Data Hub
Development of a Trusted Research Environment (TRE) compliant with the European Health Data Space. The Hub enables the exploration and analysis of multimodal cohort data while preserving patient confidentiality. - Digital Twin Conceptual Map Visualization
Integration of interactive conceptual maps within the CNIC Data Hub to support the design and interpretation of digital-twin models.
2. Advanced Algorithmics and AI
We design predictive, causal, and generative AI models to better understand cardiovascular risk, disease pathways, and therapeutic opportunities.
Key Projects
- Predictive Modeling and Explainable AI
- Development of risk-prediction models for identifying modifiable drivers of cardiovascular disease in young, asymptomatic individuals. PMID: 33004133
Includes the application of explainable AI (XAI) to reveal personalized risk-factor profiles.
- Development of risk-prediction models for identifying modifiable drivers of cardiovascular disease in young, asymptomatic individuals. PMID: 33004133
- Causal Inference and Phenotypic Networks
- htmed R package for mediation-based phenotypic network inference
https://github.com/Luciasanchezg/htmed - Application of structural equation modelling, Mendelian randomization, and machine-learning-based causal effect estimation to uncover individualized causal paths from health to cerebrovascular disease.
- htmed R package for mediation-based phenotypic network inference
- Large Language Models (LLMs) for Cardiovascular Research
- Benchmarking LLMs for cardiovascular biomedical knowledge tasks.
- Benchmarking vision–language models (VLMs) for structured-information extraction from clinical reports.
- CARMINA: Development of a lightweight cardiovascular-specialized retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) system.
- AI for Structural Biology and Therapeutics
- Evaluation of AlphaFold and related tools for predicting pathogenicity of variants in sarcomeric proteins.
(e.g., https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/CIRCGEN.124.004922) - Automated virtual-screening pipeline for large-scale drug-discovery applications.
- Evaluation of AlphaFold and related tools for predicting pathogenicity of variants in sarcomeric proteins.
3. High-Performance Computing (HPC)
HPC underpins all our work in multimodal AI and digital twinning.
We design scalable computational architectures and optimized pipelines capable of handling:
- large federated biomedical datasets,
- high-dimensional omics and imaging data,
- large-scale model training and simulation pipelines,
- and high-throughput virtual-screening workflows.
Our HPC developments interface directly with national infrastructures and the evolving European Health Data Space.
For details on the HPC infrastructure managed by the CNIC Bioinformatics Unit, see: https://www.cnic.es/en/investigacion/2/807/tecnologia.






